Beneath the surface of our daily routines lies a bustling ecosystem, unseen yet profoundly influential. Our gut, often dubbed the “second brain,” orchestrates a complex symphony of digestion, immunity, adn even mood regulation. As science peels back the layers of this microbial world, it becomes increasingly clear that gut health is not merely about avoiding indigestion but is a cornerstone of overall wellbeing. In this exploration, we delve into the captivating ways our digestive system shapes physical vitality, mental clarity, and emotional balance—revealing that nurturing our gut may be the key to unlocking a healthier, more harmonious life.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection and Its influence on Mental Health
Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms collectively known as the microbiome,a complex ecosystem that plays a crucial role far beyond digestion. Recent research reveals that this bustling microbial community communicates directly with the brain through the gut-brain axis, a bi-directional highway of neural, hormonal, and immune signals. This connection influences various aspects of mental health, including mood regulation, anxiety levels, and even cognitive functions. Imbalances in gut bacteria have been linked to conditions such as depression, stress, and neurodevelopmental disorders, underscoring the importance of nurturing gut health for psychological wellbeing.
Key pathways of interaction include:
- Neural signaling via the vagus nerve, providing direct interaction between the gut and brain.
- Immune modulation, where gut microbes influence systemic inflammation that affects brain function.
- Metabolic production of neurotransmitters and short-chain fatty acids that support brain health.
| Microbe Influence | Impact on Mental Health |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus | Reduces anxiety and enhances mood |
| Bifidobacteria | Improves stress resilience and cognitive function |
| Clostridium Species | Linked to inflammation and depressive symptoms |
For those eager to explore more about the gut-brain interplay and its implications on mental health, institutions such as the National Institute of Mental Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offer extensive resources and scientific updates. Cultivating a diet rich in prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber, along with stress management techniques, can help maintain a healthy microbial balance and foster emotional resilience. This dynamic gut-brain relationship is a promising frontier for therapeutic interventions and holistic mental health strategies.
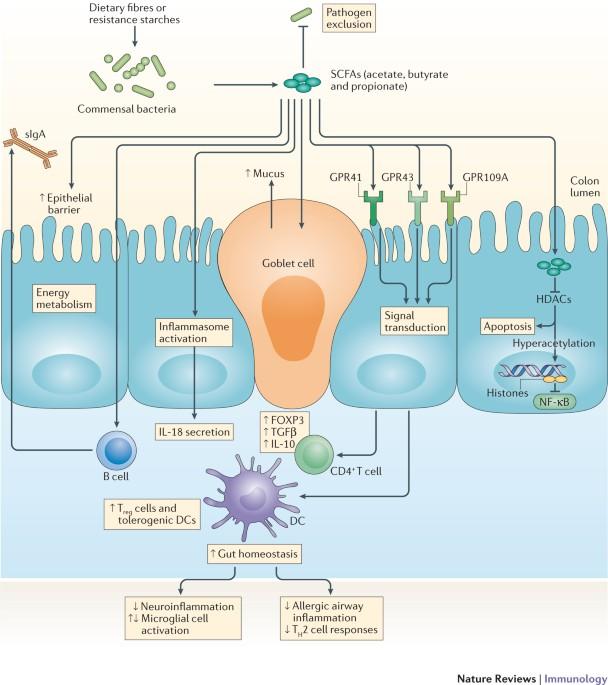
The Role of Gut Microbiota in Immune System Performance
Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms that form a complex ecosystem,playing a crucial role in shaping immune responses. These beneficial bacteria not onyl aid digestion but also act as frontline defenders, training our immune system to distinguish between harmful invaders and harmless substances. A balanced gut flora promotes the production of anti-inflammatory molecules and encourages the growth of regulatory T-cells, which help maintain immune tolerance and prevent autoimmune disorders. Disruptions to this microbial harmony, often caused by poor diet, stress, or antibiotics, can impair immune function, leaving the body more susceptible to infections and chronic inflammation.
Emerging research highlights several key functions of gut microbiota in immune support:
- Barrier reinforcement: Strengthens the intestinal lining, reducing pathogen entry.
- Antimicrobial production: Synthesizes substances that inhibit harmful microbes.
- Immune cell modulation: Influences the development and activity of immune cells.
- Metabolite generation: Produces short-chain fatty acids that fuel immune health.
| Microbiota Action | Immune Benefit |
|---|---|
| Enhancing mucosal immunity | Reduces infection risk |
| Producing anti-inflammatory agents | Mitigates chronic inflammation |
| Supporting T-cell differentiation | Prevents autoimmune diseases |
Understanding this dynamic relationship can inspire dietary choices, such as incorporating prebiotic fibers and probiotic-rich foods, to nurture a resilient immune system. For further scientific insights on gut-immune interactions, consider exploring the Nature Journal’s collection on gut microbiome and the informative resources provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
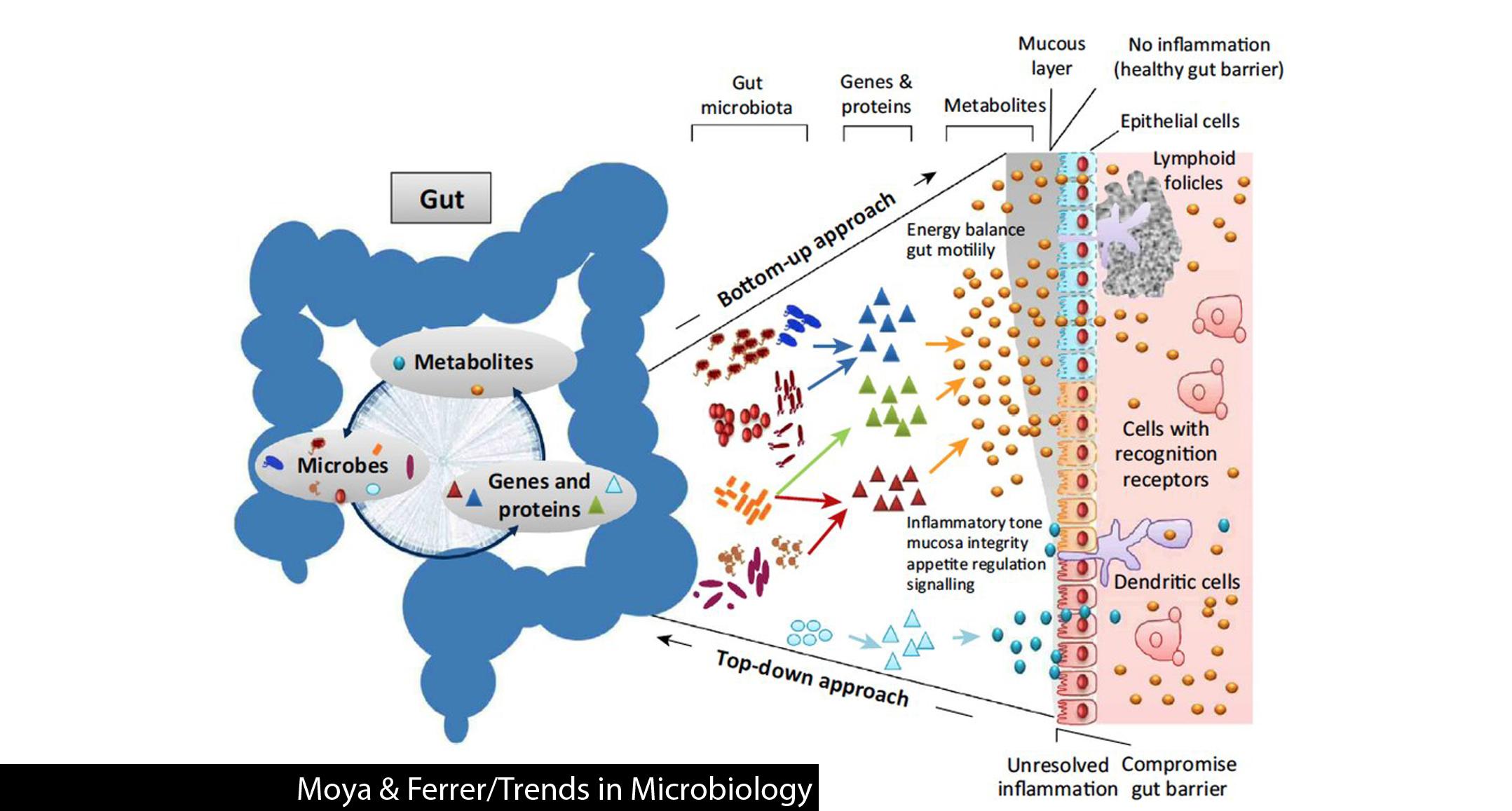
Dietary Choices That Foster a healthy Gut Environment
Maintaining a balanced gut ecosystem begins with the foods we choose to nourish our bodies. Incorporating high-fiber vegetables, fermented foods, and prebiotic-rich items supports the growth of beneficial bacteria, which play a key role in digestion and immune function. Examples include kimchi, sauerkraut, yogurt, and asparagus.By regularly consuming these foods, you help create an environment where diverse microbial communities can thrive, enhancing your gut’s resilience against harmful pathogens.
Beyond individual foods, understanding the overall dietary pattern is crucial. Minimizing processed sugars and saturated fats can prevent the overgrowth of detrimental bacteria that disrupt the gut lining and trigger inflammation. Consider the benefits of a plant-forward diet complemented by lean proteins, which not only promotes microbial diversity but also supports metabolic health.
| Food Category | Gut Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Fermented Foods | Support probiotics and digestion | Kimchi, yogurt, kefir |
| Prebiotic Foods | Feed beneficial bacteria | Garlic, onions, bananas |
| High-Fiber Vegetables | Promote gut motility and health | Broccoli, kale, carrots |
| Healthy Fats | Reduce inflammation | Avocado, olive oil, nuts |
For more details on gut-amiable dietary habits, visit resources like National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.

Practical Habits to Support Long-Term Digestive Wellness
Supporting your digestive system goes beyond occasional detoxes or trendy diets; it thrives on consistent, mindful routines that nurture your gut’s natural balance. Prioritizing hydration with filtered water, incorporating a variety of fermented foods like kimchi and yogurt, and ensuring sufficient fiber intake from whole grains and vegetables lay a strong foundation for digestive resilience. These habits feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut, fostering diversity that is key to efficient digestion and a robust immune response.
Integrating stress management techniques such as meditation or yoga can also profoundly impact your gut health, as chronic stress is known to disrupt the delicate microbiome balance.Additionally, avoiding excessive use of antibiotics and being cautious with over-the-counter medications helps prevent unnecessary harm to beneficial microbes. A simple table below outlines top daily practices for gut wellness to consider:
| Habit | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Balanced Fiber Intake | Promotes regularity &feeds gut bacteria |
| Regular Probiotic Foods | Enhances gut flora diversity |
| Mindful Eating | Reduces digestive stress |
| Stress Reduction | Prevents harmful gut-brain axis disruption |
| Moderate Antibiotic Use | Protects microbiome integrity |