Our joints are the remarkable hinges that allow us to move,bend,and dance through life’s moments with ease. Yet, these vital connections often go unnoticed until discomfort or stiffness remind us of their importance. Maintaining healthy joints isn’t just about avoiding pain—it’s about preserving the fluidity and freedom that make everyday activities a pleasure rather than a challenge. In this article, we delve into the best practices for nurturing joint health, blending science, lifestyle habits, and simple routines to help keep your movements smooth and your body strong for years to come.
Understanding Joint anatomy and Common Issues
Joints serve as the pivotal connection points between bones, allowing for versatility and movement. Each joint is a complex structure composed of cartilage,ligaments,synovial fluid,and a surrounding capsule,all working in harmony to facilitate smooth motion and absorb shock. When properly maintained, joints enable us to perform daily activities with ease. Though, they are also susceptible to wear and tear, inflammation, and injuries that can impact overall mobility and quality of life.
Common joint issues often stem from factors like aging, repetitive strain, trauma, or autoimmune conditions. Some of the most prevalent concerns include:
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage leading to pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disorder causing joint inflammation.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs cushioning joints.
- Tendonitis: Irritation of tendons around the joints.
Understanding these components and common disorders is essential to adopting a proactive approach to joint health. For a thorough overview of joint anatomy, visit the Mayo Clinic’s arthritis guide. Keeping joints healthy depends on a combination of proper movement, nutrition, and preventive care to ward off degeneration and maintain function.
| Joint Component | Function | Common Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Cartilage | Cushions bones, reduces friction | Osteoarthritis |
| Ligaments | Connect bones, stabilize joints | Sprain/strain |
| Synovial Fluid | Lubricates the joint | Inflammation |

Nutrition Strategies to Support Joint Health
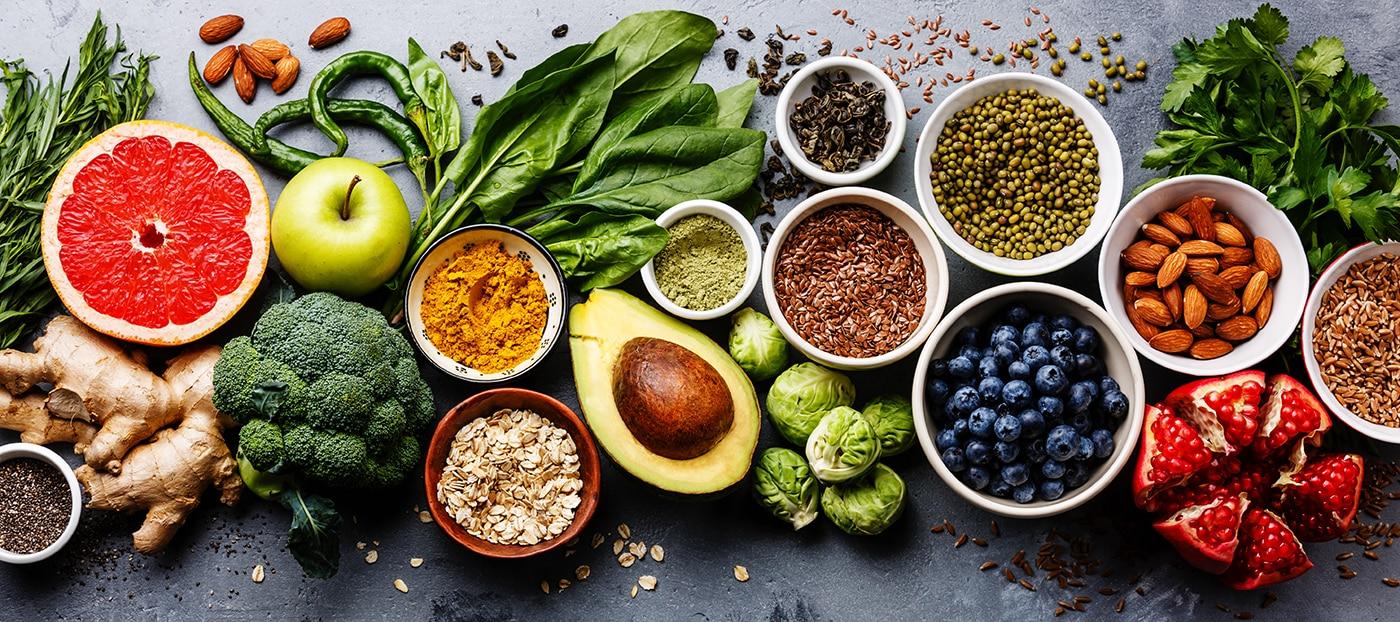
Supporting your joints from within starts with a nutrient-rich diet tailored to reduce inflammation and promote cartilage repair. Incorporate foods abundant in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, wich help diminish joint stiffness and swelling. Vitamin C-rich fruits like oranges and strawberries contribute to collagen synthesis, essential for maintaining the integrity of cartilage and connective tissues. Additionally, antioxidants found in colorful vegetables like spinach and kale protect your joints from oxidative stress, a key factor in joint degeneration.
Complementing these nutrients with specific minerals like calcium and magnesium strengthens bone health and supports muscle function around the joints. Consider integrating natural anti-inflammatory spices such as turmeric and ginger into your meals; their active compounds have been widely studied for joint comfort benefits (source). Below is a simple guide to essential nutrients and their joint-support roles:
| Nutrient | Role in Joint Health | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduces inflammation and joint pain | Salmon, Flaxseeds, Walnuts |
| Vitamin C | Collagen formation and cartilage repair | Oranges, Strawberries, Kiwi |
| Calcium and Magnesium | Bone strength and muscle support | Yogurt, Almonds, Leafy Greens |
| Antioxidants | Protects joints from oxidative damage | spinach, Kale, Blueberries |
To deepen your understanding of joint-friendly nutrition and lifestyle choices, visit trusted health resources like WebMD’s Osteoarthritis Nutrition guide and the comprehensive dietary guidelines from the NIAMS.
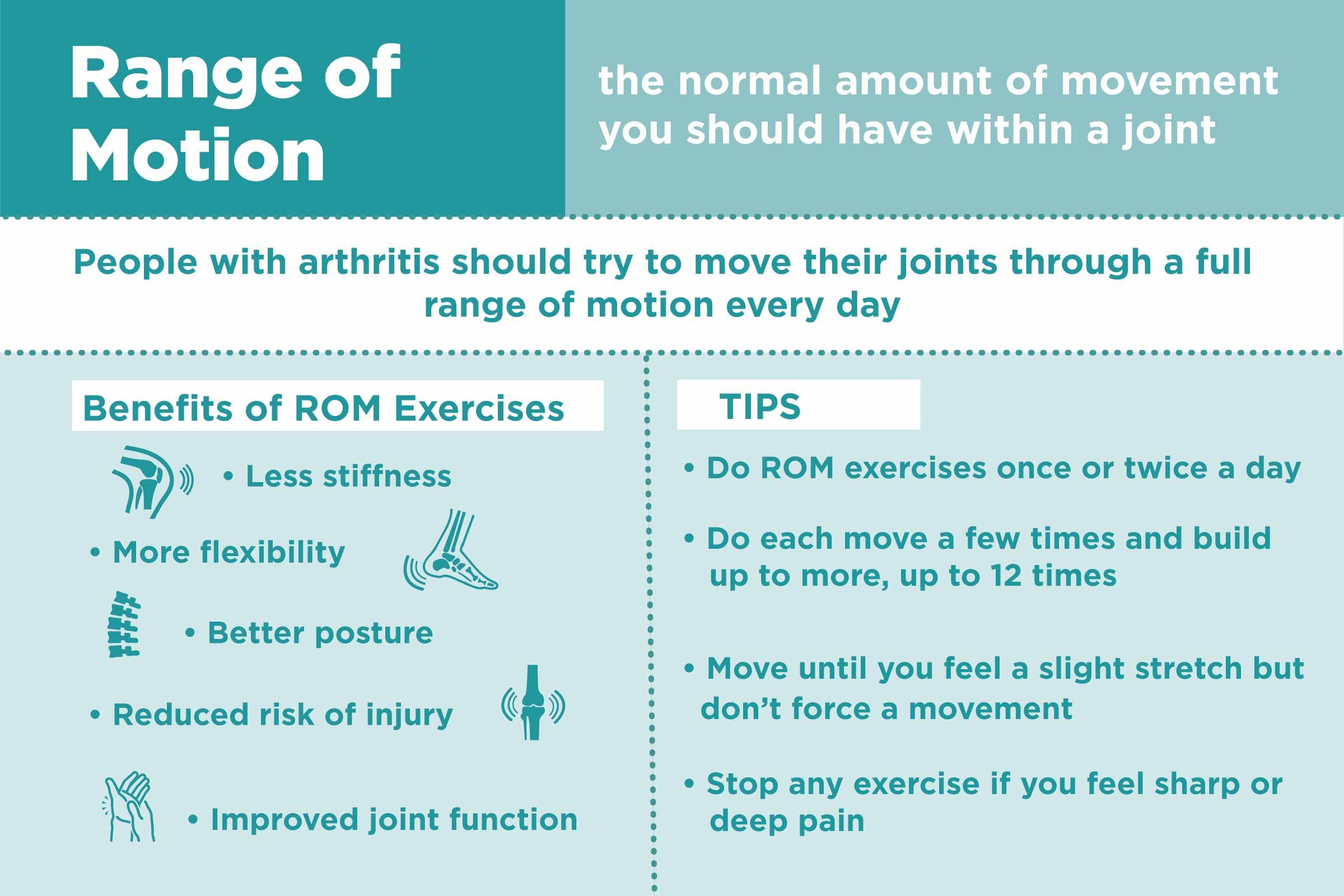
Effective Exercise Routines for Longevity
To foster lifelong mobility and joint health, incorporating a mix of low-impact exercises into your routine is essential. Activities such as swimming, cycling, and brisk walking enhance cardiovascular fitness without placing undue stress on your joints. Additionally, strength training helps support and stabilize joints by building the muscles around them, reducing the risk of injury. stretching routines focused on improving flexibility further ensure that your joints maintain their full range of motion, minimizing stiffness as you age. For personalized exercise guidance backed by scientific research, visit Mayo Clinic.
Balance and coordination exercises also play a crucial role in preventing falls and joint trauma, especially for older adults. Incorporating yoga or tai chi into your weekly rotation not only enhances joint stability but also promotes mindfulness and stress reduction, which can have indirect benefits for joint health.Below is a simple table outlining key exercise types and their joint health benefits:
| Exercise Type | Joint Benefit |
|---|---|
| Swimming | Low-impact resistance, reduces stress on joints |
| Strength Training | Muscle support for joint stabilization |
| Yoga/Tai chi | Improves flexibility and balance |
Consistently practicing these exercises, along with proper rest and joint care, sets the stage for a vibrant, active life well into your golden years. For further expert advice, consult the Arthritis Foundation.

Lifestyle Habits That Promote Joint Flexibility and Strength
Adopting daily habits that nourish your joints can substantially enhance their flexibility and strength. Incorporate a balanced routine of low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, or yoga, all known to improve joint mobility without excessive strain. Equally significant is maintaining a healthy weight, which reduces unnecessary pressure on weight-bearing joints. Consuming an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon, alongside antioxidants from colorful fruits and vegetables, supports joint health by minimizing oxidative damage and promoting tissue repair.
Integrating mindful practices such as regular stretching and strength training fortifies muscles around the joints, increasing stability and preventing injury. Adequate hydration plays a subtle but vital role in keeping the synovial fluid within joints at optimal levels, ensuring smooth movement. The table below highlights key lifestyle habits with actionable tips to optimize joint health. For further guidance on exercise regimes and nutrition plans, consult resources from the Mayo Clinic and the National Institutes of Health.
| Habit | Benefit | pro Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Low-Impact Exercise | Enhances joint mobility and muscle support | Try swimming 3x/week for a joint-friendly workout |
| Balanced Anti-Inflammatory Diet | Reduces inflammation and promotes healing | Incorporate walnuts and leafy greens daily |
| Hydration | Maintains optimal synovial fluid lubrication | Aim for 8 glasses of water throughout the day |
| Weight Management | Decreases joint stress and wear | Focus on gradual, enduring weight loss |
| Consistent Stretching | Improves flexibility and reduces stiffness | Incorporate morning and evening stretching routines |
To Wrap It Up
In the intricate dance of daily movement, our joints serve as the vital hinges that keep us agile and strong. Embracing best practices for joint health is not merely about prevention, but a commitment to nurturing our body’s natural harmony. Whether through mindful exercise, balanced nutrition, or a posture-conscious lifestyle, each small step contributes to lasting comfort and mobility. By tending to our joints with care and attention, we pave the way for a future where every motion feels fluid and pain-free—allowing us to move through life with ease and grace.





